barfoed's test principle|Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and : Clark Barfoed’s test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of cupric (II) acetate to cuprous (I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms a brick-red precipitate. [To Parent Directory] 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 776 BARs.aspx 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 5859 BARs.aspx.cs 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 1456 BARs.aspx.designer.cs 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 133891 BARs.Designer.cs 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 130016 BARs.rdlc 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 361 BARs.xsc 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 14751 BARs.xsd 8/2/2024 11:17 AM 848 BARs.xss
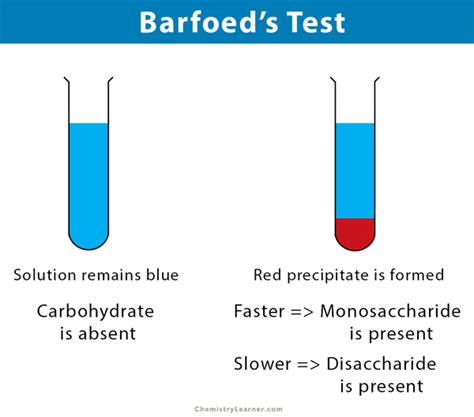
barfoed's test principle,The Barfoed reagent is made up of copper acetate in a dilute solution of acetic acid. Since acidic pH is unfavorable for reduction, monosaccharides, which are strong reducing agents, react in about 1-2 min. However, the reducing disaccharides take a . Tingnan ang higit paImage Reaction Source: Chemistry Learner, Created with BioRender.com. 1. The presence of red precipitate detects the presence of reducing monosaccharides in the . Tingnan ang higit pa
Barfoed’s test is a chemical test used to detect the presence of monosaccharides which detects reducing monosaccharides in the presence of disaccharides. This reaction . Tingnan ang higit paBarfoed’s test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of cupric (II) acetate to cuprous (I) oxide (Cu 2 O), which forms a brick-red precipitate.
Barfoed’s test is a biochemical test used to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution. The technique was devised by a Swedish physician C. .
Barfoed's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of copper(II) acetate to copper(I) oxide (Cu2O), which forms a brick-red precipitate. RCHO + 2Cu + 2H2O → RCOOH + Cu2O↓ + 4H (Disaccharides may also react, but the reaction is much slower.) The aldehyd.
Principle. Barfoed’s test reaction is based on the reduction of cupric acetate by reducing monosaccharides and reducing disaccharides. Reduction of cupric . Principle of Barfoed’s test: Barfoed’s test is used for distinguishing monosaccharides from reducing disaccharides. Monosaccharides usually react in about 1-2 minute while the reducing .Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and Barfoed’s Test In this part of the experiment, you will again test known samples of glucose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, starch, and compare with a sample of a .Barfoed’s test is based on the reaction of reducing sugars with copper acetate in a dilute acetic acid solution. The copper acetate acts as an oxidizing agent that accepts .How to perform the test: One ml of a sample solution is placed in a test tube. Three ml of Barfoed's reagent (a solution of cupric acetate and acetic acid) is added. The solution is .A biochemical test to detect monosaccharide (reducing) sugars in solution, devised by the Swedish physician C. T. Barfoed (1815–99). Barfoed's reagent, a mixture of ethanoic . Principle: Barfoed’s test is a simple and rapid test used for the identification of monosaccharides. In this test, a sample is heated with Barfoed’s reagent (a mixture of copper acetate and acetic acid) in a boiling water bath. Monosaccharides (such as glucose, fructose, and galactose) reduce the copper ions in the reagent to form a red . PRINCIPLE: Barfoed’s test differs from benedict’s test in an aspect that reduction is carried out in acidic medium. Since the medium is unfavorable for reduction, Only the strongly reduced .Barfoed’s test: A chemical test known as the Barfoed's test is used to identify the presence of monosaccharides and can identify reducing monosaccharides when disaccharides are present. Disaccharides might be used in this reaction, although it would proceed extremely slowly. A diluted acetic acid solution of copper acetate Cu (CH 3 . Principle of barfoed’s test: When barfoed reagent mix with solution of monosaccharide or disaccharide, and heated in boiling water bath, they react and crystal precipitate is formed. Copper acetate which is present in barfoed’s reagent convert to copper oxide and give brick red precipitate when react with monosaccharide or .

Barfoed’s test Principle: At the point, when barfoed’s reagent mixes with series of monosaccharide or disaccharide and warmed in bubbling water shower, they react and a precious stone solution is formed. Copper acetic acid derivation which is available in barfoed’s reagent of copper oxide and gives block red solution when it . To start the test, take a test tube and add 5 ml of Seliwanoff’s reagent in it. Make sure that the amount of reagent you are adding in the test tube doesn’t exceed 5 ml and measure it before pouring it. Now the material which is to be tested, pick it up, measure 1 ml of it and pour it down in the test tube. The third step should be to heat .
Principle. Barfoed’s test reaction is based on the reduction of cupric acetate by reducing monosaccharides and reducing disaccharides. The free aldehyde and ketone groups of monosaccharide reduce copper sulfate to cuprous oxide and give red precipitates. Reagent. To 450 mL of boiling water, add 24 g of copper acetate.
Benedict’s Test Principle When a reducing sugar is subjected to heat in the presence of an alkali, it gets converted into an enediol (which is a relatively powerful reducing agent). Therefore, when reducing sugars are present in the analyte, the cupric ions (Cu 2+ ) in Benedict’s reagent are reduced to cuprous ions (Cu + ). Principle: In Barfoed’s test, the copper ion in the solution oxidizes the reducing monosaccharide to form a carboxylic acid and copper (I) oxide, resulting in the formation of a red coloured precipitate. Procedure: 1 mL of the solution to be tested + 3 mL of freshly prepared Barfoed’s reagent; Place test tubes in a boiling water bath for 3 .barfoed's test principle In principle, for all these methods, a (salt-free) solution containing carbohydrate material is treated with a specific reagent, generating a characteristic-colored reaction product that is proportional to the sugar concentration. . 4.3.7 Barfoed’s Test. Barfoed’s test is used to detect the presence of reducing monosaccharides in solution .The Barfoed’s test is a chemical technique that determines whether or not a sample contains simple sugars. Barfoed’s reagent is a particular liquid that we can mix with the sample and heat to examine if the liquid changes color. If the sample becomes reddish-brown in color, it indicates the presence of monosaccharides, which are simple sugars.
Barfoed’s test makes use of Barfoed’s solution, which contains copper acetate in the dilute acetic acid with a pH of 4.6. Principle: In Barfoed’s test, the reducing monosaccharide is oxidized by the copper ion in the .Barfoed’s test Barfoed’s test mainly used for detecting the presence of mono-saccharides or disaccharides in the given sample. Principle The reduction of cupric acetate by reducing monosaccharides and disaccharides is the base of Barfoed’s test reaction. Cupric acetate is reduced to cuprous oxide, which results in a brick red colour . Principle of Bial’s Test. This test is based on the principle that under hydrolysis pentosans are hydrolyzed into pentoses. Further, pentoses are dehydrated to yield furfural, which in turn condense with orcinol to form a blue-green precipitate. In the presence of hexoses, hydroxyfurfural is formed instead of furfural which upon .
Principle. This test is based on the reaction of alpha-naphthol with carbohydrates in the presence of sulfuric acid. The sugars react with alpha-naphthol in an acidic environment to form purple-colored furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural derivatives. . Barfoed’s Test. It is a differentiating test to distinguish between monosaccharides and .barfoed's test principle Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and Principle of Seliwanoff’s test. The reagent of this test consists of resorcinol and concentrated HCl. The acid hydrolysis of polysaccharides and oligosaccharides yields simpler sugars. Ketoses are more rapidly dehydrated than aldoses. Ketoses undergo dehydration in the presence of concentrated acid to yield 5-hydroxymethyl furfural. Take two clean dry, test tubes and add 1 ml of the test solution/sample in one test tube. Similarly, take 1 ml of distilled water in another test tube to act as control. Add 2 ml of Tollens’ reagent to both test tubes. Keep both the test tubes in a water bath for at least 2 minutes. Observe the development of color in the test tube.
Barfoed’s Test 2. You will again test glucose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, starch, and your unknown. Add 1 mL of the solution to be tested to each of 6 labeled test tubes. Add 3 mL of Barfoed’s reagent to each of the 6 test tubes, and mix each tube thoroughly by shaking the tube. Place these tubes in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes. .
barfoed's test principle|Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and
PH0 · Experiment
PH1 · Carbohydrates
PH2 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Reagents & Result Interpretation
PH3 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and Result
PH4 · Barfoed’s Test: Principle, Procedure, Reaction, and
PH5 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Reagents,
PH6 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results And
PH7 · Barfoed’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results And
PH8 · Barfoed’s Test
PH9 · Barfoed's test
PH10 · Barfoed's Test